On-grid Solar system
- Home
- Solutions
- Solar Solutions
- On-grid Solar system

In an on-grid Solar system, the solar system is connected to the local utility GRID, so the utility system in your building will be a battery space.
This system is beneficial in case the solar panels generate more than what is needed, as you don’t need an expensive battery back-up system. Excess energy is transferred to the local grid power company (net metering), building credit in your account to cash out on an annual basis.
In some countries there is a process called Gross metering, where all solar energy produced is exported to the electricity grid.
This system depends on solar inverters or micro-inverters, however, batteries can be added if needed.
On-grid Solar system components
Solar panels (solar modules)
Silicon-based photovoltaic cells (PV cells) are used to make current solar panels that are connected to adjacent panels through cables, they are used to produce direct current electricity from sunlight/ irradiance, not heat.
The energy produced depends on solar panels orientation and tilt angle, efficiency, energy loss due to shading, dirt and ambient temperature.
Solar Inverter
This part is responsible for converting direct current (DC) electricity to alternating current (AC).
There are two main types of inverters; string inverter systems where the solar panels are tied together in a series, and micro inverters where there is a separated micro-inverter attached to the rear of each panel.
Some modern string inverter systems use a power optimizer to monitor and control each panel separately to ensure maximum efficiency.
Batteries
There are many types of solar energy storage batteries such as redox flow batteries and sodium-ion batteries; however, lead-acid (AGM & Gel) and lithium-Ion batteries are the most common.
Many shapes and sizes are available from rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, which are used in most energy storage systems. This type can supply up to 90% of their available capacity per day, and it can be discharged fully in emergency backup situations.
On the other hand, to increase battery life, lead-acid batteries only supply 30% - 40% of their total capacity per day.
Electricity Switchboard
In an on-grid solar system, the switchboard receives AC electricity from the solar inverter and sends it to different circuits and appliances.
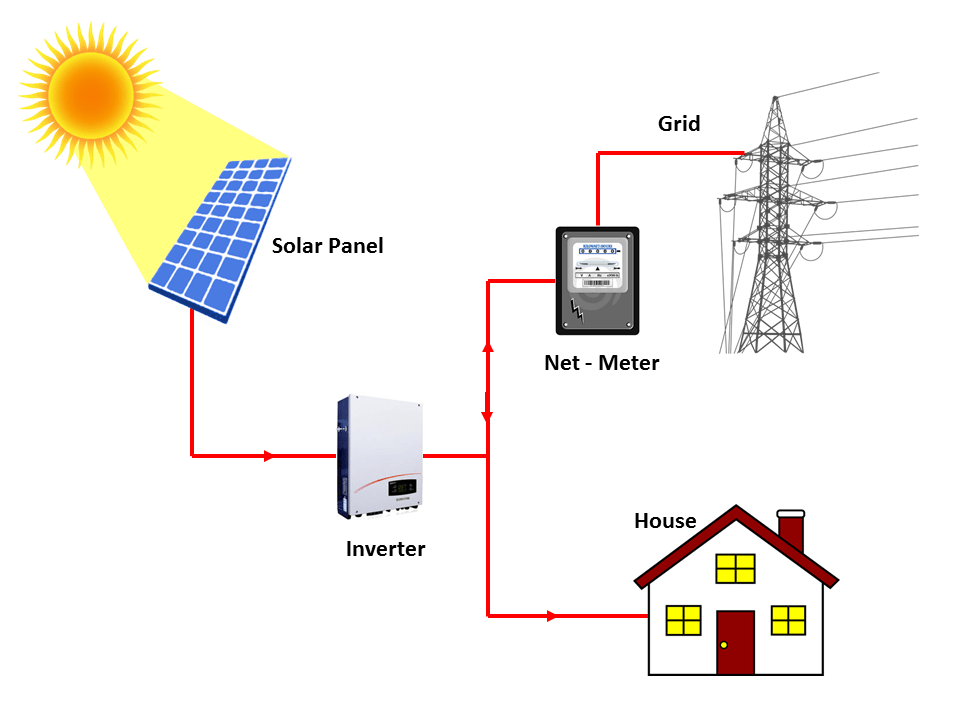
How On-grid Solar system works
In this system, the panels absorb the sunlight and transfer it to the inverter, which is sent to the switchboard.
After the electricity reaches the switchboard it goes through:
- The meter: which calculates how much solar energy will be exported (sent to grid) or imported (purchased).
- Electricity grid: which receives the extra electricity from your system that can be used by other users on the grid. It also can provide your system with needed electricity, in case your system hasn’t generated enough energy.
On-grid Solar system benefits
- Cost-effective
- Easy installation
- In 3-4 years, businesses can get back what they invested in the system, by offsetting electricity their bills.
- Residential users and business owners can gain extra income by selling extra energy generated.
Applications
The system can be used to supply businesses and residential buildings daily energy requirements.

Number of solar panels needed to run a building
The number of solar panels needed to run a building depends on several factors:
- Time spent in the building
- Average annual energy consumption
- Does your country encourage and allow Net Metering
Alternatives in the market
- Off-grid solar system (stand-alone power system- SAPS)
- Hybrid solar system
